Unit 2: Future Impact of AI
Comprehensive Overview of Potential Future Impacts of AI, Both Positive & Negative in Education, Workforce, & Daily Life

Artificial Intelligence in Education
Educators must “help the next generation face the reality of the world and develop instruments and ways of navigating this reality with integrity,” Houman Harouni.
AI technologies like data analytics, machine learning, and natural language processing are transforming learning processes and environments. By providing personalized instruction, interactive tutors, and adaptable platforms, AI stands to make education more accessible, engaging, and effective for diverse student needs. However, thoughtfully crafted policy and curriculum oversight is required to ensure AI equitably augments human teaching expertise rather than inappropriately replacing educators in the classroom.
As artificial intelligence rapidly progresses, effectively leveraging AI in education systems will be crucial for empowering students’ future success and opportunities. Integrating AI capabilities like personalized tutoring apps, computer vision assisted grading, and analytical learner feedback tools can dramatically augment and enhance teaching methods when thoughtfully implemented under instructor guidance. However, without mindfully cultivated AI literacy and skills to ethically interact with inevitable algorithmic advancements ahead, students risk lacking the foundation to adapt in an increasingly technology-driven job landscape where AI redefines industries.
Being able to understand how AI works is an important way to understand that AI is not perfect and uses data to form answers.
Positive Impacts
1. Artificial Intelligence needs to be used alongside students and teachers.
Engage with generative AI tools with your students in person, when possible. Otherwise, share AI-generated responses to questions during class time and ask students to consider them or have students experiment with the technology at home, document their experiences, and share them with the class. Having students critically think in classrooms due to AI asking questions or have other important info can bring positive change.
Positive Feedback Loop: AI can increase the quality and quantity of feedback provided to students and teachers, as well as suggesting resources to advance their teaching and learning. AI could help teachers stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in their field. For example, a biology teacher would have AI update them on the latest breakthroughs in cancer research, or leverage AI to update their curriculum.
AI has the potential to enhance the teaching and learning experience by providing personalized learning, automating administrative tasks, and improving student outcomes.
Students and teachers can speak, gesture, sketch, and use other natural human modes of communication to interact with a computational resource and each other. AI can generate human-like responses, as well. These new forms of action may provide supports to students with disabilities.
2. Teach students how not to be replaced by AI
Rather than viewing AI as replacing human roles, educators must leverage technology to amplify student learning in innovative ways. Harouni advocates that teachers guide students to critically evaluate AI-generated information, asking follow-up questions no robot could formulate independently. By modeling how to probe biased frameworks and incomplete answers, instructors teach vital skills AI lacks - layered reasoning, conceptual nuance, and interrogating the significance of "right" responses. Instead of directly providing ChatGPT results on a topic, educators should encourage student-driven inquiry, helping shape meaningful exploration around their curiosities. While intelligent algorithms can supply information, teachers play an indispensable role in developing the human intelligence to apply knowledge wisely. The educator's creativity comes through illuminating the rich learning opportunities possible when students are empowered to keep discovering.
3. change what learning really is
Will gen AI be like the calculator in school, or will it become a backstage weapon? In middle schools and high schools today, everywhere the students can use their calculator to speedily solve difficult problems of calculation or graphing. However, it has not resulted in the removal of basic mathematical computation from the curriculum: They can do long division, exponents and other math without computers. Students are not so stupid today as they were in the past. But, as Reich pointed out on the other hand, writing also helps one to learn how to think. Will outsourcing so much of that work to AI damage students 'critical thinking skills?
Liang suggested that students must learn about how the world works from first principles – this could be basic addition or sentence structure. However, they no longer need to be fully proficient – in other words, doing all computation by hand or writing all essays without AI support.
Rather than replacing human skills, AI could raise expectations by enabling students to think more critically and creatively, according to Demszky. Instead of memorizing facts or procedures, learners can leverage AI to generate initial content. The models do not do the students' thinking for them; the priority shifts to editing, evaluating, and curating model outputs. As Khan notes, this empowers students to become architects pursuing ambitious projects versus simply demonstrating basic proficiencies. When freed from repetitive tasks, students can dedicate energy towards higher-order goals that drive deeper engagement. AI may redefine mastery itself by requiring learners to interpret, refine and advance algorithmic suggestions. The models feed student agency rather than stifle it, expanding growth opportunities through purposeful collaboration with technology.
And Noah Goodman, associate professor of psychology and of computer science, questioned the analogy, saying this tool may be more like the printing press, which led to democratization of knowledge and did not eliminate the need for human writing skills
Negative Impacts
1. One of the biggest negative impacts of AI is that outputs do not reflect true cultural diversity.
ChatGPT falls severely short in authentically reflecting the identities and experiences of marginalized student groups. As Levine highlighted, when prompted to mimic the voice of a Black female author, ChatGPT simply inserted slang without grasping the cultural context or lived reality behind such communication. This failed attempt exposes the AI's lack of true understanding of the oppression and struggles minority youth face. Yet diversity and representation are fundamental for an equitable, inclusive education. When algorithms generate text oblivious to nuances of code-switching, when machine learning design excludes non-majority participation, underserved learners can feel alienated rather than empowered by technology. Until more diverse data trains systems like ChatGPT and diverse teams build them, AI risks harming the vulnerable students who most need to see their histories, languages, and lives valued in learning environments. Ethical AI integration requires not just preventing outright biased harm, but advancing anti-racist, elevating solutions. There is profound risk as well as opportunity in shaping how future intelligent systems recognize and respect multicultural strength.




Dora Demszky
Dora Demszky
There is no doubt that artificial intelligence will profoundly reshape education. As algorithms grow more advanced at producing written content, mathematical solutions, and analyzing sources, AI has the potential to transform how students learn and teachers teach. However, while intelligent technology can augment and enhance human capabilities, the core value of education - nurturing creativity, critical thinking, and collaboration - will remain essentially human. Students still need guidance making meaningful connections, asking thoughtful questions, and putting knowledge into wider context. AI cannot replicate the nuanced back-and-forth discussions that build deeper conceptual understanding. And promoting inquiry, imagination, and innovation requires empathetic instructors who know how to inspire, not just inform. So while artificial intelligence models will generate promising educational applications, from personalized assessments to interactive simulations, the essence of impactful learning is not just information delivery but equipping learners to solve complex problems collaboratively. Thus, responsible integration of AI should aim to amplify student potential rather than attempt to mimic the collective skills that set human cognition apart.
2. AI can be wrong but it will look like its right
While advanced AI models like ChatGPT may achieve 95% accuracy on certain tasks, the 5% error rate still poses risks when applied to sensitive domains like education. Even occasional mistakes or false information from such powerful language models can negatively shape student perspectives during pivotal learning stages. And when AI confidence outpaces its true dependability on emerging tasks, misunderstandings around reliability may propagate misplaced trust in algorithmic output. Proactive measures are thus essential to confirm technical transparency and prevent assumed infallibility, upholding human guidance surrounding appropriate usage where developmental impacts warrant abundant care.
3. AI is going to effect Plagiarism, Ethics, and Bias and misinformation. Although we are covering it in another unit, this is very important to address in education.

AI in the Workforce
"While AI would likely take away 85 million jobs globally by 2025, it would also generate 97 million new jobs in fields ranging from big data and machine learning to information security and digital marketing." - World Economic Forum.
Artificial intelligence refers to software and machines that can perform tasks normally requiring human cognition, allowing businesses to automate certain jobs and augment human capabilities. As machine learning algorithms enable computers to independently improve at predicting behaviors, recognizing patterns, understanding language, and making decisions based on data, AI is transforming processes and workflows across many industries. Experts predict AI and automation will redefine the future workforce as people increasingly collaborate with smart systems on analysis, creativity, service roles, and higher-order responsibilities requiring human judgment.
AI getting rid of low labor repetitive jobs
As artificial intelligence systems grow more advanced at pattern recognition, process automation, and prediction through self-learning algorithms, a widening range of rote cognitive and manual labor occupations stand susceptible to replacement by AI. Jobs involving highly structured or repetitive data tasks like transportation, administrative work, financial services, and manufacturing carry heightened vulnerability of being reassigned from human employees to efficient AI solutions in the coming decade.
One important example is Amazon. 750,000 Amazon robots are doing the heavy lifting for our employees so they can deliver for customers. With the latest in AI, our technology makes our sites safer and enables employee upskilling.
Tech titan Amazon recently announced the elimination of over 18,000 jobs, the biggest in the company's history
New jobs coming due to AI
As AI matures, several new professions will emerge to support, optimize, and oversee these powerful systems. AI trainers will educate models while AI operators handle real-time tuning for organizational needs. Data engineers will feed and manage the immense data fueling next-generation AI. With language models generating unverified content, fact checkers will validate quality, accuracy and originality of outputs before usage. Ethics specialists will govern responsible system development so AI aligns with human values.
Specialized AI integrators will seamlessly incorporate intelligent algorithms into company workflows through customized configurations maximizing value-add. Strict monitoring for model bias and unfairness will likely necessitate algorithm auditors to uphold standards of fairness and transparency. As laws evolve around emerging technologies, dedicated legal experts will ensure compliance across operationalization.
Creative roles like VR developers, personality designers and AI experience curators will humanize interactions by crafting immersive simulations and relatable digital personas. Talent development leads will construct comprehensive AI training programs equipping employees to utilize these ever-advancing tools. And overseers like prompt engineers will optimize language model functioning for organizational initiatives through expertise in best prompt practices and code quality assurance.
Democratized access to powerful AI will also drive new startup possibilities, allowing small founding teams to launch innovative ventures once inconceivable without vast technical resources. Though not without risks, AI propels promising potential across industries when anchored by human creativity, ethics and security considerations.
Needed skills that AI can't take over

Creativity
Creativity is key to all kinds of freelance work. Writers, designers, marketers, and many others need to demonstrate polished creative skills to succeed. And the benefits of creativity aren’t just limited to producing content. AI only can use data that is was given so it can not become original.

Interpersonal
Beyond expertise in their field, thriving freelancers cultivate vital interpersonal abilities allowing them to actively listen, read emotional cues, confidently negotiate terms, and nurture strong client relationships over time through adaptability and empathy. This high degree of "people skills" fuels not only directly commissioned work but expanding professional networks and referrals, as excellent communications and rapport readily earn trust and respect.

Critical Thinking
Critical thinking empowers evaluating information quality while considering multi-dimensional impacts of decisions. This judicious analysis entails investigating issues from diverse lenses, envisioning potential consequences on stakeholders given contextual insights, and leveraging past patterns to better tackle emerging challenges. By transcending narrow perspectives, critical thinking illuminates overlooked aspects and crafts balanced, ethical way forward.

Leadership
Leadership in the workplace involves complex social interactions and emotional intelligence that require uniquely human capabilities. While AI can provide data to support decision making, relating to employees and inspiring them requires empathy and interpersonal skills that only humans possess. Though AI will take over some routine tasks, the ability to develop talent, drive creativity, and motivate teams to come together around a unifying vision is rooted in intuitive aspects of human nature that machines lack.

Humane
Humane qualities like compassion and understanding involve complex social interactions and emotional intelligence that require uniquely human capabilities. While AI can provide data to support decision making, relating to employees with kindness and building an ethical culture requires empathy and interpersonal skills that only humans possess. Though AI will take over some routine tasks, the ability to support personal growth, nurture positive relationships, and cultivate communities based on shared values is rooted in intuitive aspects of human nature that machines lack.
Job Market
Uneven Global Impact
Developing countries are likely to face greater workforce disruption as a higher percentage of roles focus on routine manual or clerical tasks that are more susceptible to automation. While new technology jobs appear safer currently as AI still lacks sufficient real-world knowledge, developing countries often lack the educational infrastructure to retrain displaced workers. This growing skills and opportunity gap means developing nations must invest quickly in digital literacy and advanced IT training programs, otherwise technology change could exacerbate existing inequalities and unemployment levels.
The Gig Economy & AI-Driven Freelancing
The gig economy and AI-driven freelancing platforms offer workers flexibility in setting their own hours and choosing projects, but may lack job security and benefits. While the freedom of freelancing is appealing and enables work-life balance, income volatility and the lack of traditional employee benefits like health insurance create precarious employment conditions for gig workers. Additionally, as AI and automation take on more basic tasks, human freelancers may face increasing competition against artificial intelligence, driving down wages over time across knowledge industries. Policymakers will need to address this growing segment of contingent workers and pass legislation that extends some employee protections and benefits to them if gig work continues displacing traditional employment arrangements.
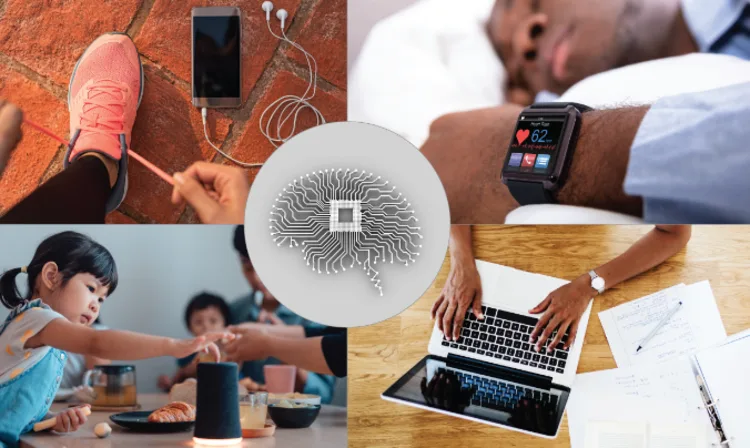

AI in Daily Life
AI is becoming integrated into many everyday products and services to provide greater personalization, convenience and efficiency. Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa rely on natural language processing to understand voice commands, while mobile apps leverage machine learning to customize content to individual interests and behaviors. As AI capabilities continue to advance, more mundane daily tasks like driving, shopping, and home maintenance may become automated as well, freeing up humans to focus less on routine activities and more on creative pursuits that provide joy and fulfillment.
AI in Homes
Amazon Alexa is an intelligent virtual assistant that uses natural language processing to understand verbal requests and respond conversationally to carry out tasks. People can interact with Alexa devices like Echo smart speakers in their homes to access information like weather and news hands-free, control smart home devices, make purchases, set reminders, listen to music or audiobooks, and more through simple voice commands. With Alexa's ability to understand natural speech, learning and remembering user behaviors and preferences, and connecting individuals to a vast range of services via the cloud, this AI assistant has provided helpful automated assistance for many daily activities in a seamless, convenient way.
AI in suggestions
AI-driven recommendation systems on platforms like Netflix and Amazon significantly influence our content consumption and shopping choices by anticipating our preferences and curiosities. These systems enhance user experiences by providing personalized suggestions tailored to our tastes based on our previous viewing and purchase histories, as well as aggregated data models. However, because they are optimized to promote engagement and sales, recommendation algorithms can also lead consumers down narrow paths of suggested items and create "filter bubbles" that limit serendipitous discoveries of new interests.
AI in driving
Tesla Autopilot is an advanced driver assistance system that uses cameras, sensors and artificial intelligence to enable vehicles to steer, accelerate and brake automatically within their surrounding environment. Autopilot's computer vision and neural network machine learning algorithms can detect lane markings, read road signs, recognize objects near the car and respond appropriately based on training data. While Autopilot features enhance safety and convenience for drivers, they still require human supervision as the AI technology has limitations navigating all complex road conditions and making ethical decisions in hazardous situations.
AI in Healthcare
Healthcare faces mounting workforce shortages, with projections indicating over 6 million providers could leave jobs by 2026 while only 1.9 million new hires may enter to replace them. Implementing AI to automate workflows presents solutions, potentially mitigating scarcity while reducing fatigue and improving cost-efficiency.
One major opportunity lies in streamlining prior authorizations (PAs). Today's manual PA processes burden staff across organizations, who must submit and review custom paperwork to treat patients, causing delays and complications. Intelligent robotic automation using natural language processing and machine learning can ingest requests and approvals, determining outcomes rapidly. Cloud-based ePA systems with AI can alleviate administrative hassles, enabling clinicians to deliver timely, quality care. Though technology alone cannot resolve all healthcare's HR challenges, optimized AI assistance maximizes limited person-power to aid providers serving more patients.
Education:
https://www.gse.harvard.edu/ideas/usable-knowledge/23/07/embracing-artificial-intelligence-classroom
https://tech.ed.gov/ai/
https://hai.stanford.edu/news/ai-will-transform-teaching-and-learning-lets-get-it-right
https://www.inspiringinquiry.com/learningteaching/technology/ai-in-the-classroom
https://www.commonsense.org/education/articles/chatgpt-and-beyond-how-to-handle-ai-in-schools
Workforce:
https://www.cbsnews.com/news/ai-job-losses-artificial-intelligence-challenger-report/
https://www.businessinsider.com/job-disruption-ai-future-careers-blue-collar-desk-work-2023-11
https://knowadays.com/blog/3-important-soft-skills-that-ai-cant-replace/#:~:text=In%20this%20post%2C%20we'll,Critical%20thinking
Daily Life:
https://www.forbes.com/sites/premier/2023/11/02/beyond-the-hype-four-ways-artificial-intelligence-is-transforming-healthcare/?sh=5ca61d6e2a2a